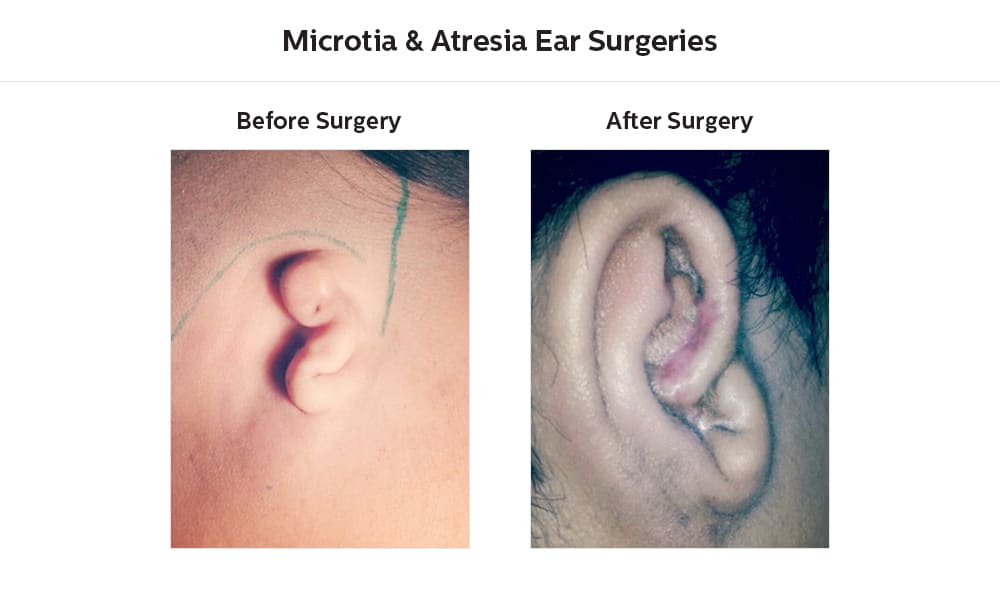
Introduction
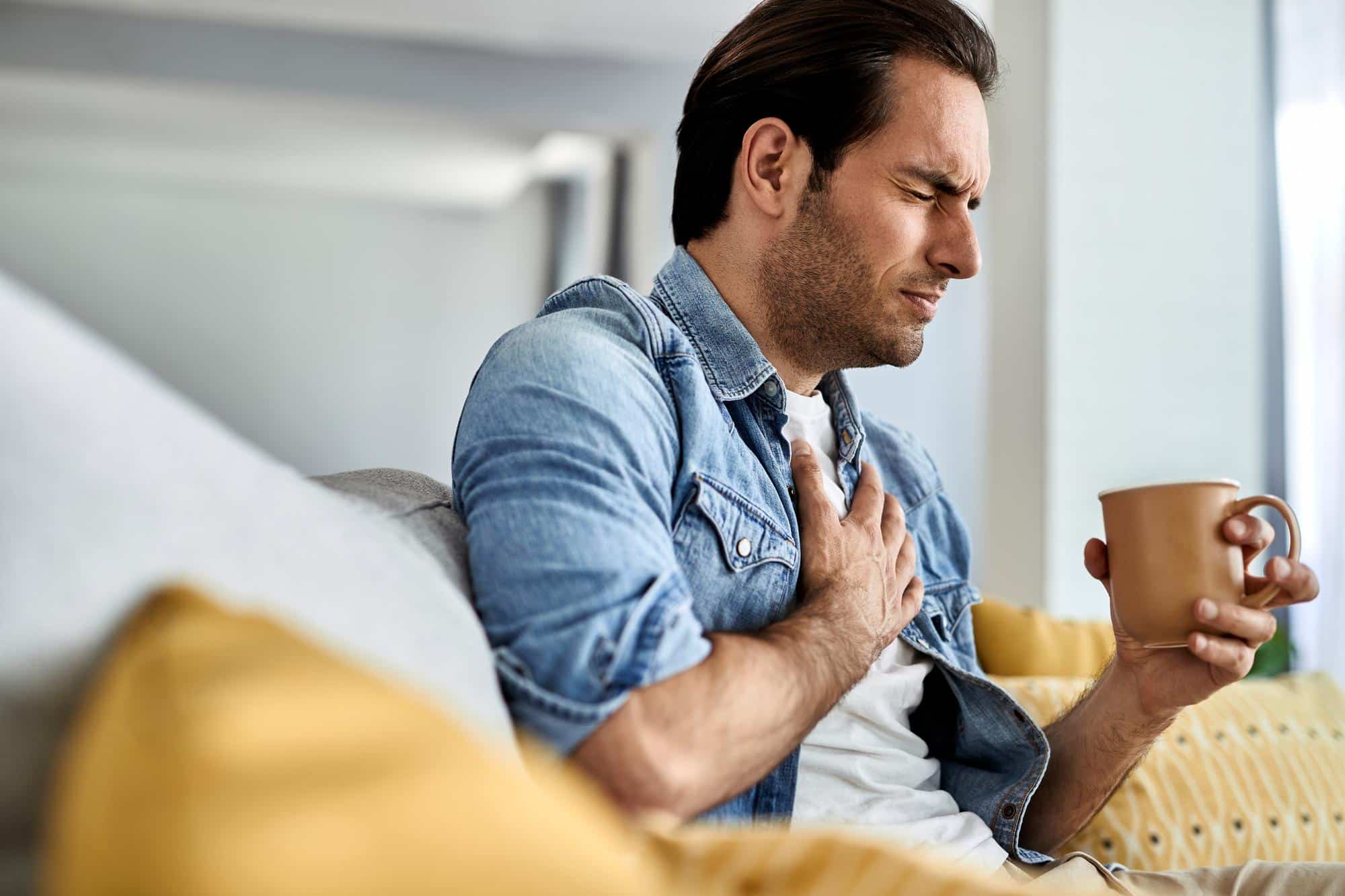
Heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, are one of the leading causes of death worldwide. They occur when blood flow to the heart is blocked, depriving the heart muscle of oxygen and causing damage. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, account for nearly 17.9 million deaths annually, making them a significant public health concern.Raising awareness about the causes and symptoms of heart attacks is crucial for early detection, prevention, and timely medical intervention. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of heart attacks, their causes, symptoms, and risk factors, empowering readers to take proactive steps toward better heart health.
Understanding Heart Attacks
What Is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot or a buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the coronary arteries. This blockage prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart muscle, leading to tissue damage or death if not treated promptly.
The Physiological Process
- Plaque Formation: Over time, cholesterol and other substances accumulate in the walls of the coronary arteries, forming plaques.
- Rupture and Clotting: If a plaque ruptures, it triggers the formation of a blood clot at the site.
- Blocked Blood Flow: The clot can partially or completely block blood flow, causing a heart attack.
This process is often the result of coronary artery disease (CAD), the most common cause of heart attacks.
Causes of Heart Attacks
Heart attacks are caused by a combination of lifestyle factors, genetic predispositions, and underlying health conditions. Understanding these causes can help individuals reduce their risk.
-
Lifestyle Factors
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk of obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes, all of which are linked to heart attacks.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, reduces oxygen in the blood, and accelerates plaque buildup.
-
Genetics and Family History
- A family history of heart disease significantly increases the likelihood of developing heart-related issues. Genetic factors can influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and other risk factors.
-
Underlying Health Conditions
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Puts extra strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
- High Cholesterol: Excess LDL (“bad” cholesterol) contributes to plaque formation in arteries.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
-
Stress and Mental Health
- Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating or smoking, which increase heart attack risk. Stress hormones can also raise blood pressure and heart rate.
-
Age and Gender
- The risk of heart attacks increases with age, particularly after 45 for men and 55 for women. While men are more likely to have heart attacks, women often experience different symptoms, making diagnosis more challenging.
Symptoms of Heart Attacks
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack is critical for seeking timely medical attention. Symptoms can vary between individuals and may not always be severe.
Common Symptoms
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as pressure, tightness, or a squeezing sensation in the chest.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, which may occur with or without chest pain.
- Pain in Other Areas: Pain or discomfort may radiate to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some individuals, especially women, may experience nausea or indigestion-like symptoms.
- Cold Sweats: Sudden sweating without physical exertion.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness, particularly in women, can be an early warning sign.
Gender and Age Differences
- Women: More likely to experience symptoms like nausea, fatigue, and back or jaw pain rather than the classic chest pain.
- Older Adults: May have milder symptoms or attribute them to aging, delaying medical care.
Recognizing these symptoms early can save lives. If you or someone you know experiences these signs, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing heart disease and experiencing a heart attack.
- High Blood Pressure
- Damages arteries over time, making them more prone to plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol
- Excess LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque formation, narrowing arteries and restricting blood flow.
- Smoking
- Increases blood pressure, reduces oxygen levels, and accelerates arterial damage.
- Diabetes
- High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Obesity
- Excess weight strains the heart and contributes to high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Lack of exercise weakens the heart and increases the risk of obesity and related conditions.
- Stress
- Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy habits and directly impact heart health.
Preventative Measures
- Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Quit Smoking: Seek support to stop smoking and reduce your risk significantly.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Regular Checkups: Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels regularly.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Heart attacks are medical emergencies that require immediate attention. Call emergency services if you or someone else experiences:
- Severe chest pain lasting more than a few minutes.
- Pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, or jaw.
- Shortness of breath, nausea, or fainting.
Time is critical. The sooner treatment is administered, the better the chances of survival and recovery.
Conclusion
Heart attacks are a serious health concern, but understanding their causes and symptoms can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their heart health. By addressing risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and stress, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing a heart attack.If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of a heart attack, don’t delay—seek medical attention immediately. At Mahavir Jain Hospital, we are committed to providing expert care and guidance to help you maintain a healthy heart.Take charge of your heart health today. Schedule a checkup with our cardiology experts and learn how to keep your heart strong and healthy for years to come.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns. You may also check out our experts at Mahavir Jain Hospital